Bên cạnh Line Chart, Bar Chart và Table, Pie Chart cũng là một dạng biểu đồ quen thuộc, thường xuyên xuất hiện trong Writing Task 1. Cách xử lý dạng bài biểu đồ tròn có điểm tương đồng và cũng có những điểm khác biệt so với các loại biểu đồ khác. Bài viết này sẽ cung cấp cho bạn cách viết Pie chart hiệu quả nhất, giúp bạn có thể áp dụng trong bài thi IELTS thật.
Nội dung chính
1. Giới thiệu về Pie Chart
Pie Chart là một biểu đồ có dạng hình tròn, được chia thành các lát cắt để minh họa theo tỷ lệ phần trăm. Trong biểu đồ tròn, độ dài của cung tỷ lệ thuận với giá trị phần trăm mà nó biểu thị. Phần cung càng lớn thì giá trị biểu thị càng lớn. Trong Writing Task 1, bạn có thể gặp hai loại biểu đồ Pie Chart chính.
Loại thứ nhất là đề bài chỉ có một biểu đồ tròn duy nhất (Loại này tương đối ít gặp).
Loại thứ hai thường gặp hơn – đề bài có sự biến đổi theo thời gian. Loại này thường biểu thị sự lên xuống về giá trị theo thời gian của các hạng mục được biểu thị. Loại thứ hai khá phức tạp và khó xử lý hơn nhiều so với loại thứ nhất.
Xem thêm: Cách viết dạng advantage & disadvantage
2. Cách viết Writing Task 1 Pie Chart
2.1. Phân tích đề và lên dàn ý
Phân tích đề luôn là bước đầu tiên và quan trọng nhất khi làm bài Writing, đặc biệt là Writing Task 1. Với dạng Pie Chart, khi phân tích đề, bạn cần lưu ý các điều sau:
- Có bao nhiêu biểu đồ tròn trong đề bài? Các biểu đồ biểu thị hạng mục gì?
- Biểu đồ có sự thay đổi về thời gian hay không? Địa điểm biểu đồ biểu thị là ở đâu?
- Đơn vị của biểu đồ là gì?
- Sau khi xác định các yếu tố cơ bản của biểu đồ, bạn tiếp tục chú ý tới các chi tiết:
- Có sự tăng, giảm gì về giá trị của các hạng mục?
- Giá trị lớn nhất, giá trị nhỏ nhất
- Các điểm đặc biệt trong biểu đồ (các giá trị bằng nhau, các giá trị gấp đôi, …)
Biểu đồ có sự biến đổi về thời gian
“The charts below show the results of a questionnaire that asked visitors to the Parkway Hotel how they rated the hotel’s customer service. The same questionnaire was given to 100 guests in the years 2005 and 2010.
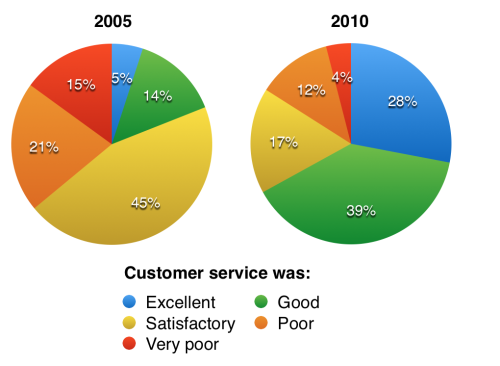
- Có hai biểu đồ trong đề bài. Cả hai biểu đồ đều thể hiện sự đánh giá của khách hàng về dịch vụ nhà hàng.
- Biểu đồ có sự thay đổi về thời gian. Địa điểm được biểu thị cụ thể là khách sạn Parkway.
- Đơn vị của biểu đồ là %
Các điểm nổi bật:
- Năm 2005: đa phần khách hàng cảm thấy dịch vụ khách sạn thỏa mãn (satisfactory) hoặc dịch vụ kém (poor);
- Năm 2010: đa phần khách hàng cảm thấy tốt (good) hoặc xuất sắc (excellent)
- Phần trăm khách hàng cảm thấy tốt (good) và xuất sắc (excellent) tăng qua 5 năm.
Biểu đồ không có sự biến đổi theo thời gian
“The chart below shows the results of a survey of people who visited four types of tourist attractions in Britain in the year 1999.”
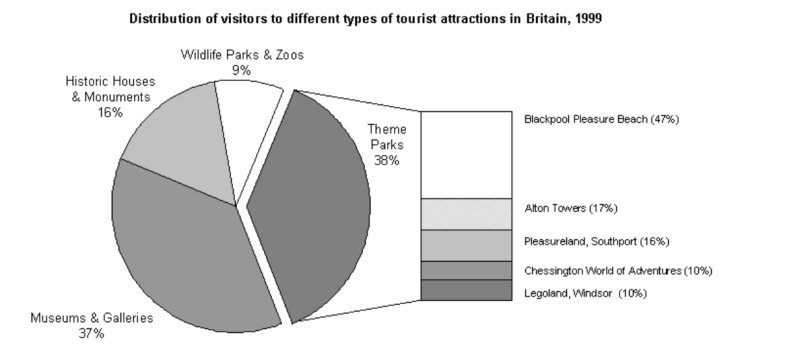
- Đề bài có 1 biểu đồ chính, 1 biểu đồ phụ. Biểu đồ chính đề cập tới lượng khách du lịch tới các khu vực giải trí, biểu đồ phụ biểu thị cụ thể lượng khách du lịch tới các Theme Parks.
- Biểu đồ không có sự biến đổi về thời gian, địa điểm là tại Anh.
- Đơn vị của biểu đồ là %.
Các điểm nổi bật:
- Theme Parks và Museums & Galleries thu hút được nhiều khách du lịch nhất, trong khi Wildlife Parks and Zoos có lượng khách ít nhất
- Blackpool Pleasure Beach là Theme Parks thu hút được nhiều khách du lịch nhất
Xem thêm: Cách “ăn điểm” dạng bài Opinion Essay
2.2. Cấu trúc bài viết pie chart
Sau khi phân tích đề một cách kỹ càng, bạn có thể chuyển sang bước lập dàn ý cho bài viết. Cấu trúc bài viết trong Pie Chart cũng tương tự với các dạng biểu đồ khác, bao gồm 3 phần chính: Introduction, Overview và Body.
Về phần Introduction, bạn chỉ đơn giản paraphrase lại đề bài.
Với Overview, bạn luôn luôn chú trọng đầu tiên tới xu hướng chính trong biểu đồ. Nếu biểu đồ không có xu hướng (không có thời gian), bạn có thể nêu ra giá trị lớn nhất hoặc giá trị nhỏ nhất.
Về phần Body, nếu biểu đồ chỉ có một Pie Chart duy nhất, bạn sắp xếp và miêu tả thông tin từ lớn nhất đến nhỏ nhất. Nếu trường hợp có hai hay nhiều biểu đồ, bạn có thể làm theo các bước sau đây:
- Đánh dấu các hạng mục được thể hiện trong biểu đồ theo xu hướng bằng các mũi tiên lên, xuống hoặc không thay đổi
- Chia các hạng mục theo từng nhóm để so sánh và đối chiếu
- Miêu tả thông tin thành hai đoạn thân bài một cách mạch lạc và logic. Lưu ý các điểm đặc biệt của biểu đồ như các giá trị bằng nhau, gấp đôi, gấp ba,…
2.3. Viết bài pie chart
Sau khi đã có được dàn ý chi tiết, bạn có thể bắt tay ngay vào việc viết bài. Tương tự với các dạng bài khác, bạn chỉ nên dành khoảng 15 phút cho quá trình viết bài.
Ví dụ về biểu đồ có sự biến đổi về thời gian
Introduction
Paraphrase lại đề bài: bạn có thể paraphrase theo một trong hai cách: word by word hoặc new structure. Tuy nhiên, cách word by word đơn giản và phổ biến hơn.
Ví dụ
The charts below show the results of a questionnaire that asked visitors to the Parkway Hotel how they rated the hotel’s customer service = “The pie charts compare visitors’ responses to a survey about customer service at the Parkway Hotel in 2005 and in 2010.”
Overview
- “It is clear that overall customer satisfaction increased considerably from 2005 to 2010.”
Sự hài lòng của khách hàng về dịch vụ khách sạn có xu hướng tăng từ năm 2005 đến năm 2010.
- “While most hotel guests rated customer service as satisfactory or poor in 2005, a clear majority described the hotel’s service as good or excellent in 2010.”
Năm 2005: đa phần khách hàng cảm thấy dịch vụ khách sạn thỏa mãn (satisfactory) hoặc dịch vụ kém (poor); Năm 2010: đa phần khách hàng cảm thấy tốt (good) hoặc xuất sắc (excellent)
Body
- “Looking at the positive responses first, in 2005 only 5% of the hotel’s visitors rated its customer service as excellent, but this figure rose to 28% in 2010.”
Tỷ lệ khách hàng đánh giá xuất sắc (excellent) chỉ khoảng 5% vào năm 2005, tăng lên 28% vào năm 2010.
- “Furthermore, while only 14% of guests described customer service in the hotel as good in 2005, almost three times as many people gave this rating five years later.”
Tỷ lệ khách hàng đánh giá tốt (good) là 14% vào năm 2005 đã tăng gấp 3 lần vào năm 2010.
- “With regard to negative feedback, the proportion of guests who considered the hotel’s customer service to be poor fell from 21% in 2005 to only 12% in 2010.”
Tỷ lệ khách hàng đánh giá kém (poor) giảm từ 21% từ năm 2005 xuống 12% vào năm 2010.
- “Similarly, the proportion of people who thought customer service was very poor dropped from 15% to only 4% over the 5-year period.”
Tỷ lệ khách hàng đánh giá rất kém (very poor) giảm từ 15% xuống 4% trong vòng 5 năm.
2.4. Kiểm tra lại bài viết
Sau khi hoàn thành bài viết, bạn nên dành ra khoảng 2 – 3 phút để kiểm tra lại. Chú ý chính tả, ngữ pháp, các động từ được chia đã đúng thì chưa. Ngoài ra, với Pie Chart, bạn nên chú ý vào các số liệu mình liệt kê trong bài viết. Đặc biệt với trường hợp có nhiều hơn hai biểu đồ, bạn dễ dàng liệt kê nhầm số liệu. Kiểm tra lại bài viết là bước vô cùng cần thiết trong cách viết Writing Task 1 Pie Chart
3. Từ vựng và cấu trúc trong cách viết Pie Chart Writing Task 1
Miêu tả Pie Chart cần một số lượng lớn từ vựng, đặc biệt từ vựng và cấu trúc miêu tả phần trăm.
3.1. Từ vựng diễn tả chiếm số lượng/ phần trăm
- To have
- be
- take
- take up
- account for
- constitute
- occupy
- amount to
- take up
3.2. Từ vựng về phần trăm
| Phần trăm | Từ vựng |
| 80% | four-fifths |
| 75% | three-quarters |
| 70% | even in ten |
| 65% | two-thirds |
| 60% | three-fifths |
| 55% | more than half |
| 50% | half |
| 45% | more than two fifths |
| 40% | two-fifths |
| 35% | more than a third |
| 30% | less than a third |
| 25% | a quarter |
| 20% | a fifth |
| 15% | less than a fifth |
| 10% | one in ten |
| 5% | one in twenty |
| 77% | just over three quarters approximately three quarters |
| 49% | just under a half nearly a half |
| 32% | almost a third |
| 75% – 85% | a very large majority |
| 65% – 75% | a significant proportion |
| 10% – 15% | a minority |
| 5% | a very small number |
3.3. Từ vựng diễn tả nhóm tuổi
- The 10 – 20 age group
- The group of 10 – 20 – years–old
- The group of/ at/ aged 10 – 20
- People at/ of/ aged 10 – 20 years old
- The 10 – 20-year-old group
Xem thêm: IELTS Writing Task 1: Cách viết biểu đồ cột (Bar Chart)
3.4. Cấu trúc miêu tả Pie Chart Writing Task 1
Cấu trúc miêu tả 1 phần biểu đồ
- Cấu trúc 1:
| The highest/ The smallest/ The lowest/ The largest/ The greatest | percen/ tage/ proportion/ quantity/ number | of + N | to be/V |
Ví dụ: “The highest number of animals was in Australia”.

- N + the most/ least + Adj + N
Ví dụ: “Brazil was the least attractive country among all nations”.
- There + be + adj + N + in + N
Ví dụ: There was an increase in the proportion of animals in Brazil.
- N + V + Adv
Ví dụ: The proportion of animals in Brazil dropped significantly in 1990.
Cấu trúc miêu tả 2 phần biểu đồ
- As many/ Twice as many/ Three times as many/ Not as many + N + to be/ V + as
Ví dụ: “In 1990, twice as many red motorbikes were produced in Brazil as in the UK.”
- More/ Far more/ Much More… + N + to be/ V + than
Ví dụ: “In 1990, much more red motorbikes were produced in Brazil than in the UK.”
- As/ Whereas/ While X verb, Y verb (at the same time):
Ví dụ: As the proportion of animals in Brazil dropped significantly, that in Poland increased.
- Clause, followed by + Noun Phrase
Ví dụ: There was a slight increase in the proportion of animals in Brazil in 1997, followed by a dramatic decrease after 10 years.
- Clause, prior to/before Verb-ing
Ví dụ: There was a slight increase in the proportion of animals in Brazil in 1997, before decreasing after 10 years.
- X verb, Verb-ing, (which verb)
Ví dụ: The percentage of mammal animals in Brazil increased to 30% in 1997, exceeding the proportion in Poland, which had only 12%.
- (Far/ Much/ Many/ Considerably/ Significantly/ Dramatically…) + more + N + to be/ V + than …
Ví dụ: Far more cars are produced in Brazil than in Austria.
- In comparison to/with X, which verb, Y verb
Ví dụ: In comparison with the percentage of animals in Brazil, which experienced a slight increase to 30,000 in 1997, the proportion in Korea dropped to 12,000 at this time.
4. Lưu ý trong cách viết Pie Chart – IELTS Writing Task 1
4.1. Dùng sai thì
Đây là lỗi sai phổ biến trong cách viết Writing Task 1 Pie Chart. Với Pie Chart, bạn nên chú ý hơn vào dạng đề bài có sự thay đổi về thời gian. Đặc biệt với đề bài có đề cập tới thời gian trong tương lai, hãy chú ý sử dụng các cấu trúc và động từ thì tương lai.
4.2. Liệt kê quá nhiều số liệu
Cho dù đề bài có đề cập tới sự thay đổi về thời gian hay không, bạn cũng không nên đề cập tới tất cả số liệu trong biểu đồ.
Để tránh việc liệt kê quá nhiều dữ liệu, bạn có thể tham khảo phần II về từ vựng trong bài viết này, đặc biệt là các từ vựng dùng để thay thế các tỷ lệ phần trăm. Ví dụ, 50% có thể thay bằng “half of” hay 77% sẽ được diễn tả bằng cụm “just over three quarters”.
4.3. Không dùng từ vựng đa dạng
Đây cũng là một trong các lỗi sai thường gặp trong Task 1, đặc biệt với dạng đề Pie Chart. Nhiều thí sinh chỉ đơn thuần liệu kê và phân tích số liệu nhưng lại không làm rõ các điểm nổi bật.
Bạn nên cố gắng sử dụng các trạng từ chỉ mức độ như “slightly, merely, significantly, dramatically, …” khi so sánh các phần hơn kém nhau. Ngoài ra, bạn cũng nên sử dụng các từ nối dùng để so sánh như “In contrast, Similarly, Likewise, …:” để làm cho bài viết trở nên mạch lạc hơn.
5. Tài liệu học Writing Task 1 Pie Chart
15 Days’ Practice for IELTS Writing
Đây là cuốn sách tổng kết tất cả các kỹ năng cần thiết cho bài thi Writing. Đặc biệt, cuốn sách được trình bày dưới dạng chia sẻ nhiều hơn, cung cấp từng bước cần thiết khi làm bài. Phần Pie Chart được năm trong chương Day 4, bao gồm đề bài, cách phân tích đề, lập dàn ý và các bài viết mẫu.
IELTS Exam Preparation
Một trang web học Writing nói chung và Writing Task 1 nói riêng khá hiệu quả. Với mỗi dạng bài, bạn đều có thể tìm thấy rất nhiều tài liệu, đề bài cũng như lời giải cho từng đề. Nếu muốn ôn luyện riêng Pie Chart, bạn có thể gõ tìm kiếm từ khóa Pie Chart trên trang web.
IELTS Advantage Writing Skill
Cuốn sách này phù hợp cho các bạn có target 7.0 trong Writing. Phần Pie Chart và Writing Task 1 nói chung nằm ở phần sau của cuốn sách. Các bài tập được liệt kê nhằm cải thiện kỹ năng xác định và phân tích đề của bạn.
6. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample
6.1. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #01
Đề bài
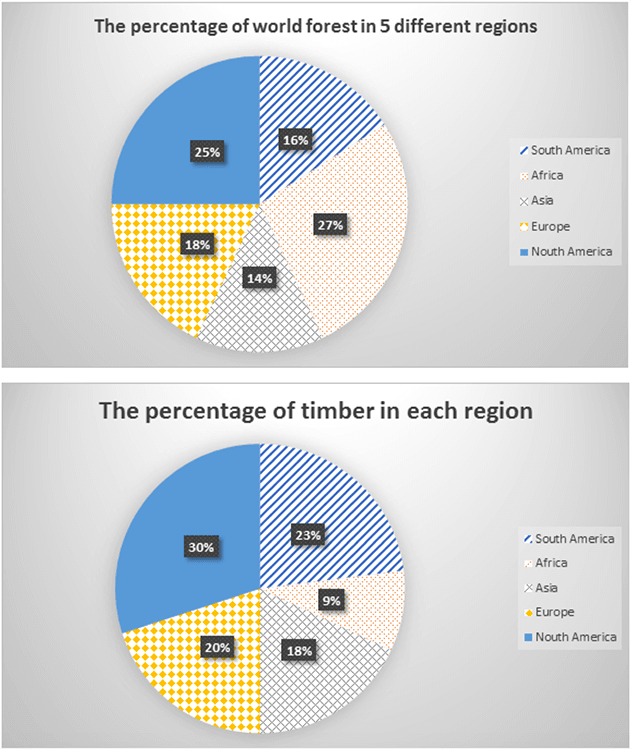
The charts below give information about the percentage of world forest and also the percentage of timber in five different regions.
Bài mẫu
The pie charts detail the distribution of global forest and also the percentage of timber in five different continents namely South America, Africa, Asia, Europe and North America. Overall, North America accounted for the highest proportions of both forest and timber production. It is also clear that Africa, despite having the largest forest cover among the five given continents, produced the smallest amount of timber.
Regarding the first pie chart, Africa constituted 27% of the total global forest, making it the most heavily forested region. North America had around 25%, and the forest cover rates of Europe, South America and Asia were a little bit less, with the figures amounting to 18%, 16% and 14% respectively.
Moving on to the second pie chart, North America produced the most timber at around 30%, which was followed by South America (23%), Europe (20%) and Asia (18%). Meanwhile, Africa’s timber production made up a negligible 9%, ranking last among the given regions.
Xem thêm: IETLS Writing Task 2: Hướng dẫn viết Cause and Effect essay
6.2. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #02
Đề bài
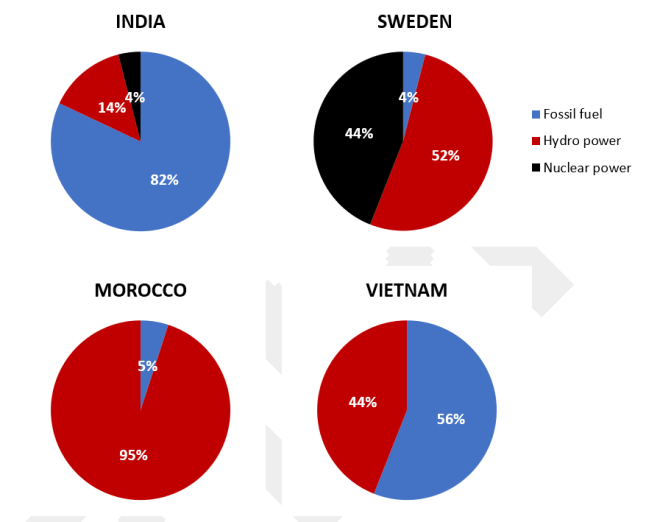
The charts show the sources of electricity produced in 4 countries between 2003 and 2008. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Bài mẫu
The given pie charts detail information about the proportion of three different sources of electricity in four countries (India, Sweden, Morocco and Vietnam) from 2003 to 2008.
Overall, Vietnam and Morocco did not use any nuclear power for electricity production. It can also be seen that while fossil fuels were the largest source of electricity supply in Vietnam and India, they only occupied a relatively marginal proportion in Morocco and Sweden during the examined years.
In Vietnam, 56% of the total amount of electricity was produced from fossil fuels, while the figure for Morocco was only 5%. The rest of the electricity, in both nations, was produced solely from hydro power.
In India however, electricity from fossil fuels contributed to 82% of the entire quantity of electricity produced, which was also the highest figure for fossil fuel use among the four countries. Meanwhile, fossil fuels were only responsible for 4% of the total generated electricity in Sweden, with hydro power and nuclear power contributing 52% and 44% respectively.
6.3. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #03
Đề bài
Bài mẫu
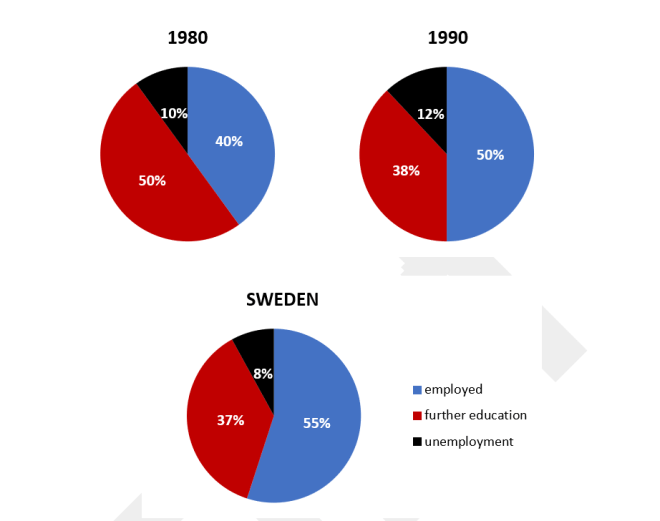
The given pie charts detail the proportion of Australian secondary school graduates who were unemployed, employed or pursuing further education, in 1980, 1990, and 2000.
Overall, from 1980 to 2000, the proportion of Australian students who were employed grew, while there was a decline in both the proportion of those pursuing higher levels of education and those who were unemployed.
In 1980, half of the Australian secondary school leavers chose to continue their education. After a 10-year period, this number dropped to only 38% and remained almost unchanged in 2000. Meanwhile, the figures for those who were unemployment were the smallest, at only 10% in 1980, 12% in 1990, and finally dropping back down to 8% in 2000.
On the other hand, over the years Australia saw an increase in the percentage of students who received a job after graduation from secondary school, from 40% in 1980 to 55% in 2000, which was the largest figure among all examined categories.
6.4. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #04
Đề bài
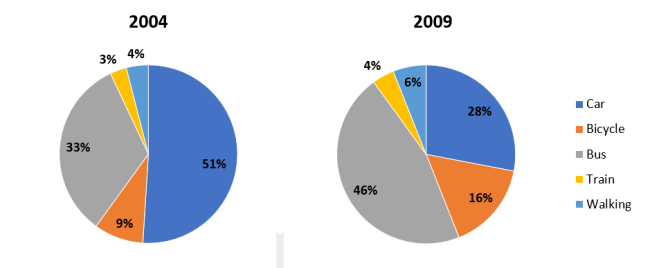
The charts show the main methods of transport of people travelling to one university in 2004 and 2009. Summarise the information be selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
* car parking charges in the university 2006
** new bus stop in the university in 2008
Bài mẫu
The given pie charts compare the percentage of students using five different means of transportation (Car, Train, Bus, Bicycle, and Walking) to travel to a particular university during 2004 and 2009.
It is noticeable that travelling by train was the least favored form of transportation, while there was a change, from cars to buses, for the most commonly used form of transport over the five year period.
In 2004, just over half of students traveled to the university by car, with only a third taking a bus. The remaining students rode a bike, went on foot or took a train, with the figures being 9%, 4%, and 3% respectively.
However, with the construction of a new bus stop in 2008 and the introduction of car parking fees in 2006, in 2009 the number of students commuting by car dropped to 28%, and consequently the number of students travelling by all other methods increased. Those travelling by bus increased to 46%, bicycle user’s rose to 16%, and both train travelers and walkers increased by 1% and 2% respectively.
Xem thêm: 19+ Bài tập thì quá khứ tiếp diễn từ cơ bản đến nâng cao
6.5. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #05
Đề bài
The pie charts indicate changes in the proportions of energy produced in a country from 1983 to 2003. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
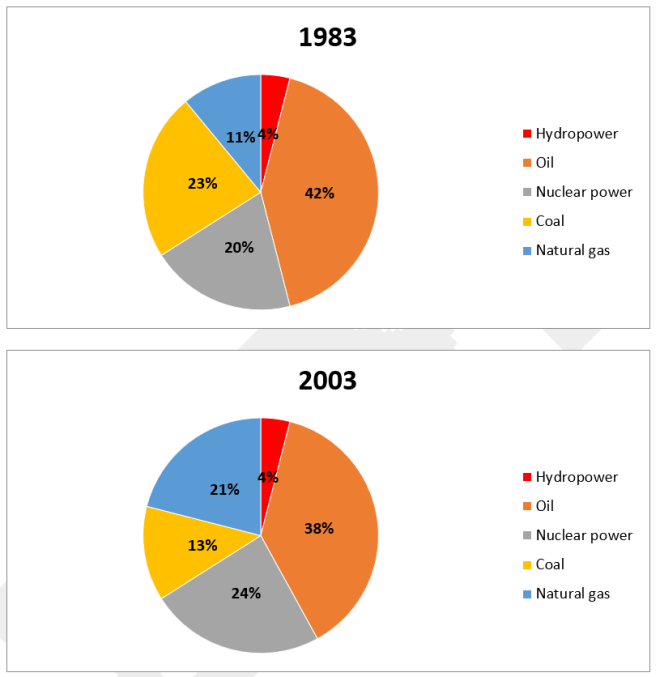
Bài mẫu
The given pie charts depict data regarding the percentage of energy generated from five different sources (Hydropower, Oil, Nuclear power, Coal, Natural Gas) in a particular country between 1983 and 2003.
In general, it is clear that oil was the most popular source of energy in both years despite a slight decrease. In addition, this country also relied more on using nuclear power and natural gas by 2003.
To begin with, in 1983, oil and coal were used to produce 42% and 23% of the total energy, respectively. Over the next 20 years, the proportion of energy produced from oil saw a slight decline by 4%, while energy from coal also reduced by 10%.
In contrast, there was a reverse pattern in both figures for nuclear power and natural gas, which increased by 4% and 10% respectively to collectively surpass the percentage of energy generated from coal. On the other hand, hydropower was responsible for only 4% of energy produced in both years.
6.6. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #06
Đề bài
The charts below show the proportion of people’s total spending in a particular European country was spent on different commodities and services in 1958 and in 2008.
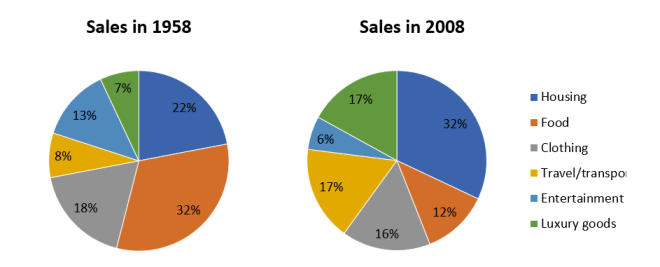
Bài mẫu
The pie charts detail the proportion of people’s total expenditure on six different goods and services (housing, clothing, entertainment, food, travel/transport, and luxury goods), in a European country, in 1958 and 2008.
It is clear from the charts that spending in all aspects, except clothing, changed quite substantially over the fifty year period.
In 1958, people spent the largest portion of their spending on food, at 32%. The two other categories that took up the majority of people’s money were housing, at 22%, and clothing at 18%. Entertainment, travel/transport and luxury goods only comprised around a quarter of all spending at 18%, 8% and &% respectively.
50 years later spending changed quite significantly with housing now becoming the biggest expense and taking up almost one third of total spending, at 32%. The expenditure on clothing, transport/travel and luxury goods all increased and all took up around 16-17% of the total spending. The expenditure on food dropped significantly to 12%, while entertainment costs were only half of that.
6.7. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #07
Đề bài
The charts below show the proportion of people’s total spending in a particular European country was spent on different commodities and services in 1958 and in 2008.
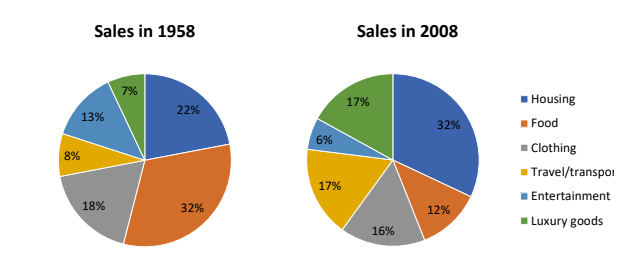
Bài mẫu
The pie charts detail the proportion of people’s total expenditure on six different goods and services (housing, clothing, entertainment, food, travel/transport, and luxury goods), in a European country, in 1958 and 2008.
It is clear from the charts that spending in all aspects, except clothing, changed quite
substantially over the fifty year period. In 1958, people spent the largest portion of their spending on food, at 32%. The two other categories that took up the majority of people’s money were housing, at 22%, and clothing at 18%. Entertainment, travel/transport and luxury goods only comprised around a quarter of all
spending at 18%, 8% and &% respectively.
50 years later spending changed quite significantly with housing now becoming the biggest expense and taking up almost one third of total spending, at 32%. The expenditure on clothing, transport/travel and luxury goods all increased and all took up around 16-17% of the total spending. The expenditure on food dropped significantly to 12%, while entertainment costs were only half of that.
6.8. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #08
Đề bài
The pie chart below shows information about where coffee is produced, consumed and where is profit goes. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
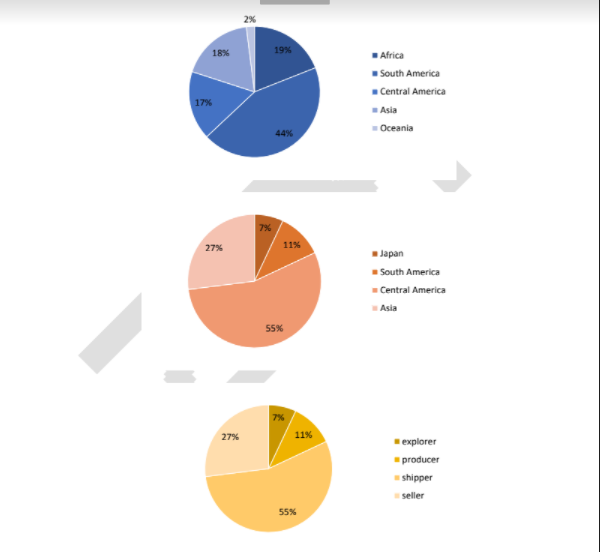
Bài mẫu
The pie charts show a breakdown of the production and consumption of coffee in particular regions, and how the profits are distributed. The initial impression from the charts is that whilst Central America is recorded to be the number one coffee producing region, it is Europe that consumed that highest amount of coffee.
Additionally, the majority of the profit earned from this industry goes to the shippers.
As far as coffee production is concerned, 44% of coffee is produced in South America, making it the leading supplier of coffee worldwide. This is followed by Africa (19%), Asia (18%) and Central America (17%).
Meanwhile, Oceania only constituted a modest 2% of the total coffee production. Regarding coffee consumption, Europeans appear to consume the most coffee, with the figure accounting for more than half. This is in marked contrast to the figures for North America and Japan at only around 10%. The remaining 27% belongs to other unspecified regions.
Profits made from the production, transport, and sale of coffee are not evenly shared among all those involved in the process. Shippers received as much as 55% of the profits, which is also the highest proportion of the profits. Sellers ranked second with 25%, while the remaining 20% is evenly divided between explorers and producers.
6.9. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #09
Đề bài
The charts below show the percentage of people aged 23-65 in different occupations in one UK town (Ashby) and in the UK as a whole in 2008.
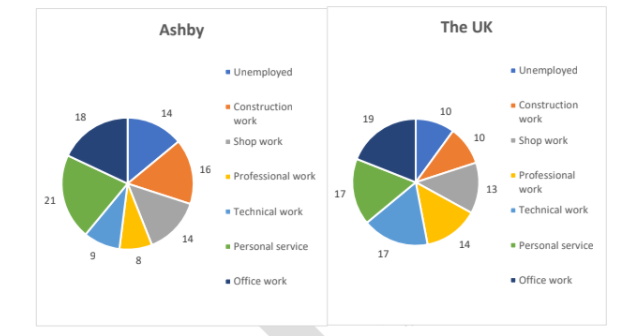
The pie charts illustrate the employment status of people aged 23 to 65, in Ashby and in the UK, in 2008.
Overall, the national unemployment rate was lower than the rate in Ashby. Moreover, while British people generally preferred office work, personal service was the most popular profession in Ashby.
The percentage of jobless people in Ashby was 14%, whereas that recorded in the whole nation was only 10%. The percentage of Ashby residents who were employed in office work and shop work were 18% and 14% respectively, similar to that of the whole of the UK, at 19% and 13% respectively.
In addition, the UK recorded a relatively high proportion of citizens employed in technical work, at 17%, while the figure for the same type of employment in Ashby was only about half that, at 9%. Furthermore, the percentage of construction workers and personal service providers in Ashby, at 16% and 21%, were both higher than the corresponding figures of the UK, at 10% and 17% respectively. Lastly, with regards to professional occupations, 8% of Ashby residents did this type of work, compared to 14% of the whole population.
6.10. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #10
Đề bài
The pie charts show the destination of export goods in three countries in 2010.
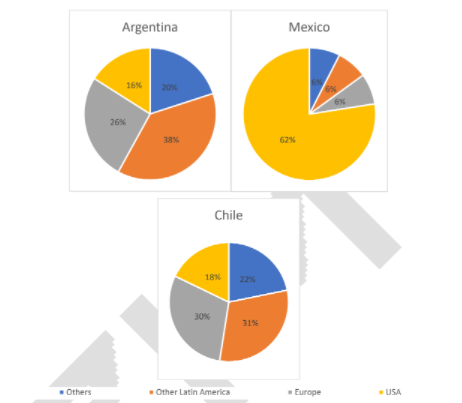
Bài mẫu
The given pie charts illustrate the percentage breakdown of goods exported from three South American countries, in 2010. It is clear that while Argentina and Chile’s exports were distributed more evenly amongst other nations, the large majority of Mexico’s exports were to the USA.
From the charts it can be seen that Argentina and Chile’s export trends were almost identical, with the majority of their exports going to other Latin American countries, at 38% for Argentina, and 31% for Chile. Meanwhile, 26% of Argentina’s exports went to Europe, 16% to the USA, and 20% to other countries. Similarly, Chile’s exports consisted of 30% to Europe, 18% to the USA, and 21% to other countries.
In contrast, the large majority of Mexico’s exports were to the USA, at 82%. The remaining exports from Mexico were to Europe, at 6%, other Latin American countries, at 6%, and other countries, also receiving 6%.
6.11. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #11
Đề bài
The three pie charts below show the changes in annual spending by a particular UK school in 1981, 1991 and 2001. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
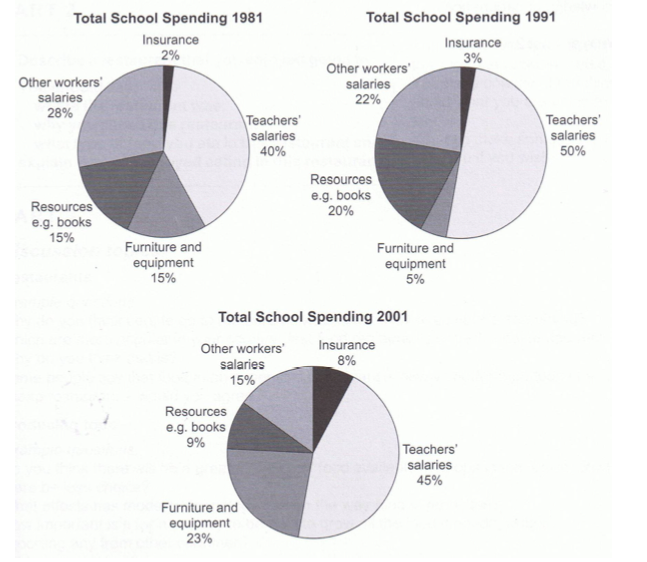
Bài mẫu
The pie charts compare the expenditure of a school in the UK in three different years over a 20-year period.
It is clear that teachers’ salaries made up the largest proportion of the school’s spending in all three years (1981, 1991 and 2001). By contrast, insurance was the smallest cost in each year.
In 1981, 40% of the school’s budget went on teachers’ salaries. This figure rose to 50% in 1991, but fell again by 5% in 2001. The proportion of spending on other workers’ wages fell steadily over the 20-year period, from 28% of the budget in 1981 to only 15% in 2001.
Expenditure on insurance stood at only 2% of the total in 1981, but reached 8% in 2001. Finally, the percentages for resources and furniture/equipment fluctuated. The figure for resources was highest in 1991, at 20%, and the proportion of spending on furniture and equipment reached its peak in 2001, at 23%.
6.12. IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Sample #12
Đề bài
You should spend about 20 minutes on this task. The pie charts show the main reasons for migration to and from the UK in 2007. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant. Write at least 150 words.
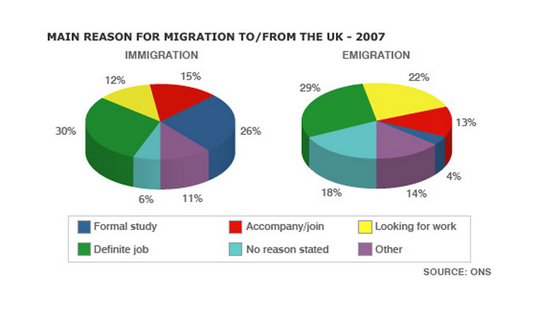
Bài mẫu
The pie charts illustrate the primary reasons that people came to and left the UK in 2007. At first glance it is clear that the main factor influencing this decision was employment.
Having a definite job accounted for 30 per cent of immigration to the UK, and this figure was very similar for emigration, at 29%. A large number of people, 22%, also emigrated because they were looking for a job, though the proportion of people entering the UK for this purpose was noticeably lower at less than a fifth.
Another major factor influencing a move to the UK was for formal study, with over a quarter of people immigrating for this reason. However, interestingly, only a small minority, 4%, left for this.
The proportions of those moving to join a family member were quite similar for immigration and emigration, at 15% and 13% respectively. Although a significant number of people (32%) gave ‘other’ reasons or did not give a reason why they emigrated, this accounted for only 17% with regards to immigration.
Cách viết pie chart đã dễ dàng hơn phần nào cho các bạn sau bài viết này rồi phải không? Ieltscaptoc.com.vn còn rất nhiều bài mẫu không chỉ của Writing Task 1 mà cả Writing Task 2 nữa đó. Ngoài ra, bạn có thể tham khảo thêm các bài học tiếng Anh bổ ích tại website ieltscaptoc.com.vn. Chúc các bạn học tập tốt.

